Techniques, Software, and Tools
Techniques
Data Scraping
Data scraping is the automated process of extracting information from websites or other online sources. This technique can be useful for collecting data from multiple sites and automating repetitive tasks. However, challenges include adapting to changes in website layouts, legal and ethical issues, and handling dynamic content (e.g. data loaded via JavaScript). For example, Python libraries such as Beautiful Soup or frameworks like Scrapy are frequently used for these purposes.
API Integration
API integration involves connecting to external services in order to retrieve structured data, often in real time. This method provides standardised data access and can streamline automated processes. Nevertheless, it requires managing API rate limits, adapting to changes in the API, and integrating data from various systems.
Data Mining
Data mining refers to the analysis of large datasets to identify patterns, correlations, and trends. This process can support data-driven decision-making, though it requires significant computational resources and expertise, and may also raise privacy concerns. Software such as RapidMiner and WEKA is commonly used in this field.
Data Wrangling/Munging
Data wrangling (or data munging) is the process of cleaning, transforming, and organising raw data into a structured format that is suitable for analysis. Although this process can be time-consuming and technically challenging, it is essential for improving data quality. Python’s pandas library is a widely used tool in this area.
Data Integration
Data integration involves combining data from different sources to create a unified dataset. This technique helps provide a comprehensive view for analysis but may involve challenges such as reconciling differing formats and schemas, and ensuring consistent data quality.
Stream Processing
Stream processing refers to analysing data in real time as it is generated. This technique is especially useful for handling time-sensitive data and high volumes of information. Tools such as Apache Kafka and Apache Flink are commonly used to manage data flows and enable real-time analytics.
Data Quality Management
Data quality management is the process of ensuring that data is accurate, complete, and consistent. High-quality data is critical for reliable analysis, although maintaining such quality requires ongoing monitoring and may be resource-intensive.
Extract, Transform, Load (ETL)
ETL stands for Extract, Transform, Load and describes the process of extracting data from various sources, transforming it into a standard format, and loading it into a target system for analysis. This approach supports data consolidation but also poses challenges in maintaining transformation accuracy and managing diverse data sources.
Software/Tools
Below is a summary table that presents some key software tools, outlining their main functions and providing examples of typical deployments or customers.
| Tool | Purpose & Function | Example Deployments/Customers |
|---|---|---|
| CKAN | Data management system for building and maintaining data hubs and portals. | Used in government open data portals such as data.gov.uk, data.gov, and various international bodies. |
| Piveau | Platform for metadata management, data harmonisation, and linked data. | Deployed in several European open data initiatives. |
| EntryScape | Enables semantic integration and linked data for complex datasets. | Mainly adopted by Swedish public organisations. |
| uData | Facilitates the publication and management of open datasets. | Employed by municipalities and local governments for open data portals. |
| OpenRefine | Tool for cleaning, transforming, and reconciling messy data. | Widely used in academic research, journalism, and by data professionals. |
| LOMAS | Allows secure processing of sensitive data with Differential Privacy. | Piloted within the Swiss public sector to enable secondary data usage while preserving privacy. |
CKAN
CKAN is an open source data management system developed by the Open Knowledge Foundation. It is designed to support the creation and maintenance of data hubs and portals, offering a standardised platform for publishing and accessing datasets. CKAN employs a PostgreSQL database, a Solr index, and a comprehensive API to facilitate data discovery and integration (see its GitHub repository for more technical information). It has been deployed widely in national and local government open data portals (for example, data.gov.uk and data.gov), as well as by various international organisations
Piveau
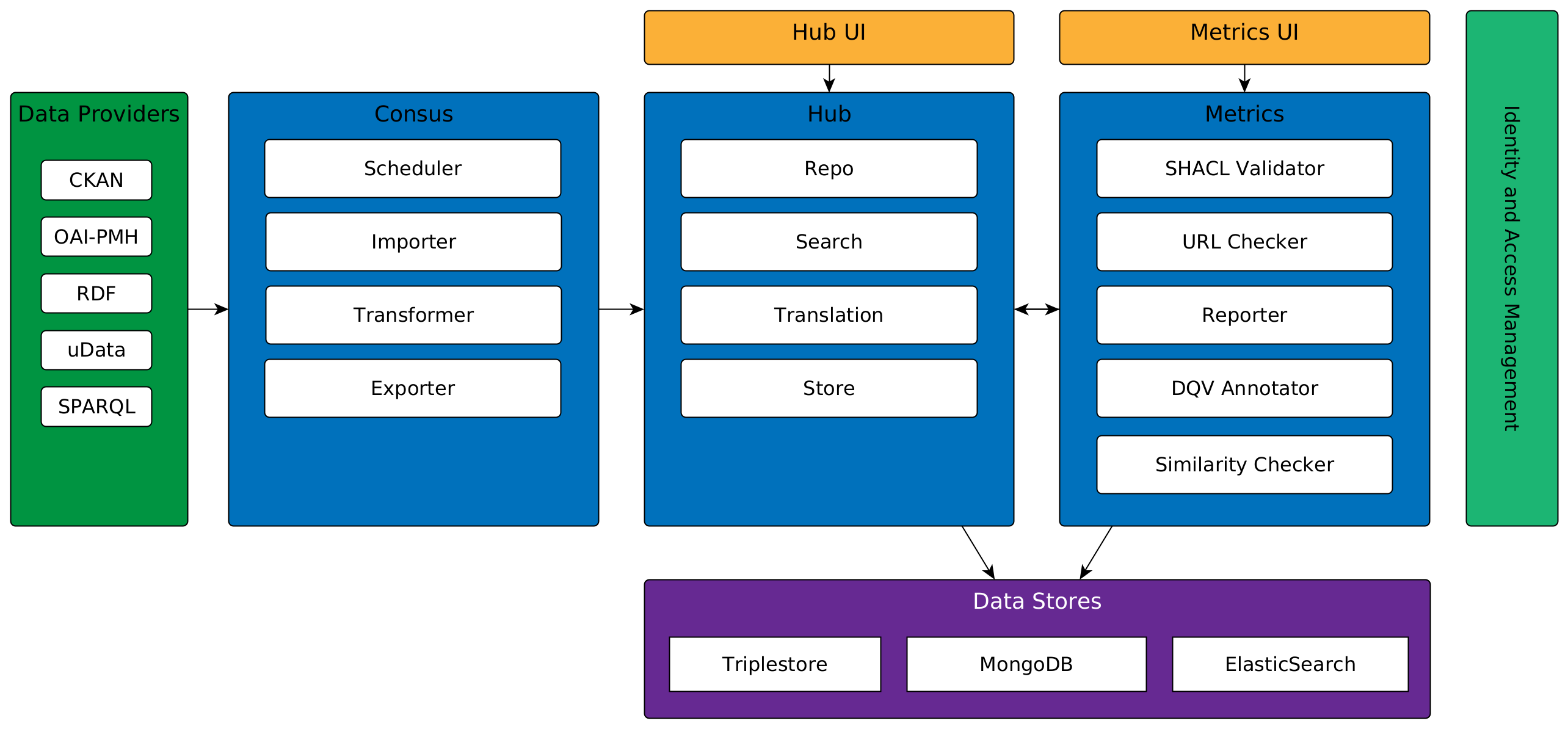
Piveau is an open data platform comprising several integrated components that focus on the management and integration of open data, with a particular emphasis on metadata management, data harmonisation, and linked data capabilities (Kirstein et al., 2020). It supports a wide range of data protocols and formats—including OAI-PMH, RDF, CKAN, uData, OwnCloud, JSON, SPARQL, Socrata, and Drupal—allowing for dynamic, programmable data transformation using JavaScript or XSLT. Harvesting processes can be individually scheduled, and the platform provides export capabilities into DCAT(-AP) and related standards.
Key features include:
Data Acquisition and Transformation:
Piveau supports scalable harvesting (up to hundreds of thousands of datasets per source) and flexible, configuration-based orchestration, enabling custom processing steps and integration with third-party services.Linked Data and Storage:
It stores DCAT metadata as RDF in a triplestore and utilises URI harmonisation to create a consistent knowledge graph. The platform also integrates external vocabularies and ontologies to enhance linked data capabilities.Search and Frontend:
A powerful search engine based on Elasticsearch and a rich, customisable, multilingual frontend allow users to efficiently search and filter metadata. Additionally, extensive backend tools facilitate the creation and management of metadata.Quality Assurance:
Piveau periodically generates quality assessments based on SHACL validations. These assessments are stored alongside the metadata using the Data Quality Vocabulary (DQV), with reports available in various formats.Access Control and Operations:
Integration with Keycloak provides robust identity and access management, while containerisation with Docker and support for Kubernetes (with ready-to-use Helm charts) ensure efficient operations. The backends are primarily written in Java and Kotlin (using the Vert.x framework), and the frontends are developed with Vue.js.
Piveau is open source and its code is available on GitLab. Below is an overview of its architecture.
EntryScape
EntryScape is an information management platform developed by Metasolutions to handle complex datasets through semantic integration and linked data principles (Ebner & Palmér, 2014). It facilitates the organisation and enrichment of heterogeneous data sources, making it easier to create interoperable and semantically rich datasets.
Its customers include a broad range of public organisations such as municipalities, regional authorities, and national agencies. For example, in Sweden, EntryScape is used by national agencies like Skatteverket or Riksarkivet. Further information is available on the EntryScape website and via its repository on Bitbucket.
uData
uData is an open data management platform developed by the Open Data Team. It aims to simplify the publication and management of data, offering a user-friendly interface that makes it accessible for both data providers and users. uData is often employed by municipalities and local governments to publish open data portals, and its modular architecture allows for easy integration with existing IT infrastructures. The source code is available on its GitHub repository.
OpenRefine
OpenRefine is an open source tool for data cleaning and transformation. Initially released in 2010 (originally as Freebase Gridworks, later renamed Google Refine), it operates as a local web application designed to help users clean messy data, standardise formats, and reconcile datasets. It supports various data formats (including CSV, TSV, JSON, and XML) and allows for advanced data manipulation using scripting languages such as GREL and Jython. For more details, see the GitHub repository.
LOMAS
LOMAS is an open source platform developed by the Data Science Competence Center (DSCC) of the Swiss Federal Statistical Office. Public services collect large volumes of data, yet strict privacy regulations often limit their secondary use. LOMAS addresses this challenge by enabling authorised users—such as approved researchers and government analysts—to execute algorithms on sensitive datasets without directly accessing the data. Instead, users submit algorithms to the platform, which then processes the data within a secure, trusted computing environment. The results are returned protected by Differential Privacy, a framework that introduces controlled noise to prevent the extraction of identifiable information. This approach allows for the quantification and control of disclosure risk while ensuring transparency about data protection (see Aymon et al., 2024).