Assessment, Data Quality, and Best Practices
Assessment
Open Data Maturity (ODM)
Since 2015, the European Union has conducted an annual assessment to gauge the progress of European countries in promoting and facilitating the availability and reuse of public sector information – predominantly open government data.
Annual Assessment
- Policy – It investigates the open data policies and strategies in place in the participating countries, the national governance models for managing open data and the measures applied to implement those policies and strategies.
- Portal – It investigates the functionality of national open data portals, the extent to which users’ needs and behaviour are examined to improve the portal, the availability of open data across different domains and the approach to ensuring the portal’s sustainability.
- Impact – It analyses the willingness, preparedness and ability of countries to measure both the reuse of open data and the impact created through this reuse.
- Quality – It assesses the measures adopted by portal managers to ensure the systematic harvesting of metadata, the monitoring of metadata quality and compliance with the DCAT-AP metadata standard, and the quality of deployment of the published data on the national portal.
For more details, please refer to the European Open Data Maturity publication.
ODM 2023
The 2023 ODM assessment involved 35 participating countries – including the EU-27, three European Free Trade Association countries (Iceland, Norway and Switzerland), and five candidate countries (Bosnia and Herzegovina, Montenegro, Albania, Serbia and Ukraine).
In 2023, Switzerland scored 79% in Open Data Maturity, ranking 24th among the participants (Page et al., 2023). Further information is available in the ODM 2023 report.
ODM 2024
The ODM 2024 assessment marks the 10th edition of this benchmarking initiative. ODM 2024 maintains the same methodology as 2023 but integrates refinements, particularly focusing on high-value datasets (HVDs), metadata quality, and portal performance (Page et al., 2024b).
Switzerland ranks 20th with an ODM score of 80 (Page et al., 2024a). Further information is available in the ODM 2024 report.
Impact Monitoring Framework
In Switzerland, the opendata.swiss platform has leveraged an Impact Monitoring Framework to assess the value of open government data initiatives. This framework employs a structured set of criteria and leverages the Social Return on Investment (SROI) approach to evaluate inputs, outputs, outcomes and overall impact. This systematic method offers a robust means to quantify the social and economic benefits derived from open data projects (Stürmer, 2016).
Data Quality and Best Practices
Data Quality
Tracking the state of open government data is crucial. Various tools are available to assess data quality: - The Open Knowledge Foundation (OKFN) Data Quality Index. - The Opquast web quality assurance checklist. - Data Quality Scores provided on platforms such as Data Winnipeg, which evaluate the metadata quality of datasets.
Best Practices and Toolkits
A number of best practice resources and toolkits help guide the effective management of open data: - The Annotated 8 Principles of Open Government Data (OGD) (US), which provide detailed guidelines. - The Open Government Data Toolkit, offering comprehensive resources for implementing open data initiatives.
These tools complement broader frameworks such as FAIR, CARE, Collections as Data, and LOUD, all of which are essential for ensuring that open data is both accessible and of high quality.
Periodic Table of Open Data Elements
The Periodic Table of Open Data Elements provides a visual summary of the enabling conditions and challenges that affect the success of open data initiatives. It outlines key elements such as:
- Problem and Demand Definition
- Capacity and Culture
- Governance
- Partnerships
- Risks
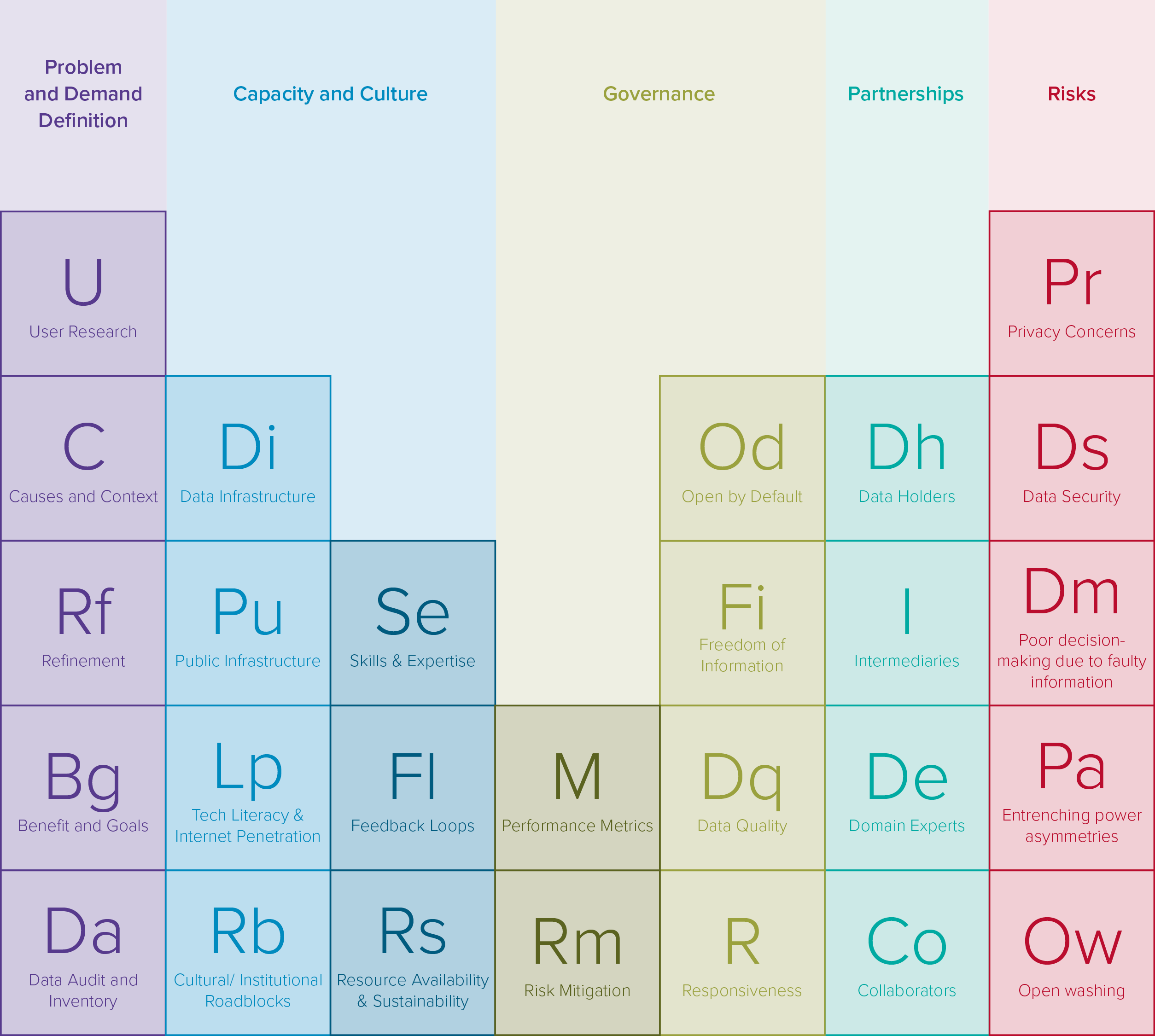
This table serves as a valuable reference for understanding the multifaceted nature of open data impacts. For further exploration, you can view the English version or the French version.